An Overview of the Nervous System and Its Functions
Understanding the nervous system is crucial for comprehending how rare neurological disorders affect the body. This lesson provides a clear and comprehensive overview to help patients and their loved ones navigate these challenging conditions.
1. Understanding the Nervous System
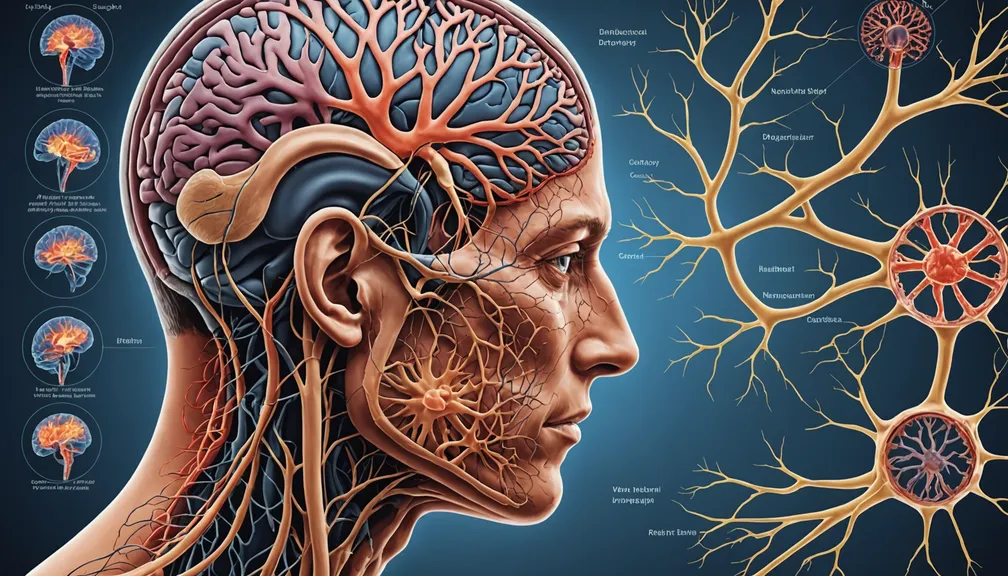
1.1 Components of the Nervous System
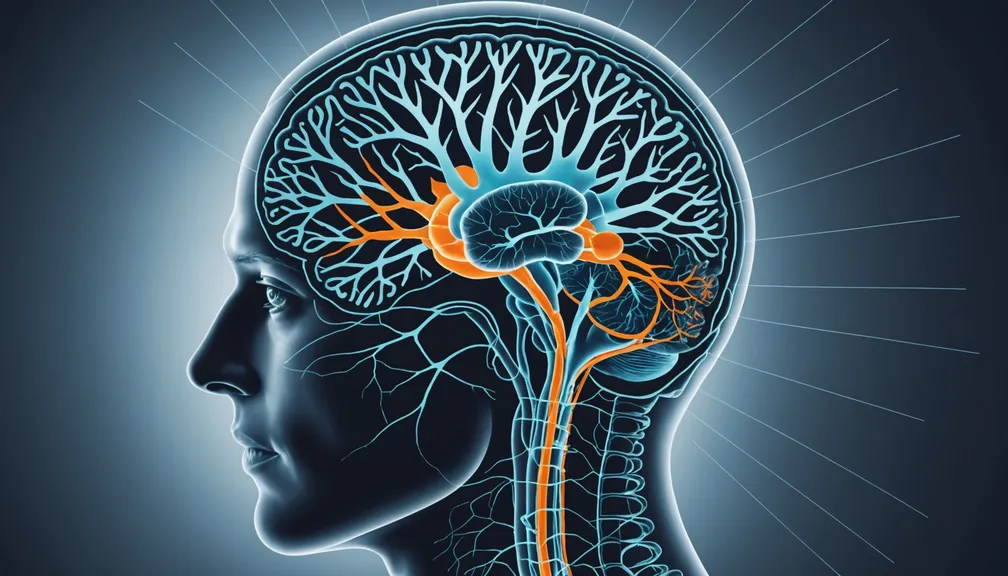
The nervous system is like the body's communication network. It consists of three main parts:
- Brain: The control center that manages thoughts, memories, movements, and emotions.
- Spinal Cord: A long, thin structure that connects the brain to the rest of the body, transmitting signals back and forth.
- Peripheral Nerves: These extend from the spinal cord to limbs and organs, allowing the brain to communicate with the entire body.
1.2 Functions of the Nervous System
The nervous system performs several essential functions:
- Sensory Processing: Detects changes both inside and outside the body, such as light, sound, touch, and temperature.
- Motor Control: Directs muscle movements and coordination.
- Cognitive Functions: Enables thinking, learning, memory, and decision-making.
- Autonomic Functions: Regulates involuntary actions like heartbeat, digestion, and breathing.
2. Rare Neurological Disorders
2.1 What Are Rare Neurological Disorders?
Rare neurological disorders are uncommon conditions that affect the nervous system. While each individual disorder is rare, collectively, they impact millions of people worldwide. These disorders can be genetic, degenerative, or result from other underlying causes.
2.2 Common Types of Rare Neurological Disorders
Some examples include:
- Huntington’s Disease: A genetic disorder causing the progressive breakdown of nerve cells in the brain.
- Multiple System Atrophy (MSA): A condition affecting movement, balance, and autonomic functions.
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome: An autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the peripheral nerves.
- Aicardi Syndrome: A rare genetic disorder primarily affecting girls, leading to severe neurological issues.
3. Impact on Daily Life
Rare neurological disorders can influence various aspects of a person's life:
3.1 Physical Challenges
- Mobility Issues: Difficulty walking or maintaining balance.
- Muscle Weakness: Reduced strength in muscles, affecting daily activities.
- Seizures: Sudden, uncontrolled electrical disturbances in the brain.
3.2 Cognitive Challenges
- Memory Loss: Difficulty remembering information or events.
- Concentration Problems: Struggling to focus on tasks or conversations.
- Communication Difficulties: Challenges in expressing thoughts or understanding others.
3.3 Emotional Challenges
- Depression and Anxiety: Feelings of sadness, hopelessness, or excessive worry.
- Mood Swings: Rapid changes in emotional states.
- Social Isolation: Withdrawing from social interactions due to physical or emotional strain.
4. Diagnosis and Treatment
4.1 Recognizing Symptoms
Early detection is vital. Common symptoms to watch for include:
- Persistent headaches
- Unexplained muscle weakness
- Unsteady gait
- Sudden vision changes
- Chronic pain
4.2 How Diagnosis is Made
Diagnosing rare neurological disorders often involves:
- Medical History Review: Understanding family history and symptom progression.
- Neurological Examinations: Assessing reflexes, muscle strength, and coordination.
- Imaging Tests: MRI or CT scans to visualize brain and spinal cord structures.
- Genetic Testing: Identifying specific genetic markers linked to the disorder.
- Electromyography (EMG): Testing the health of muscles and the nerve cells that control them.
4.3 Treatment Options
While many rare neurological disorders currently have no cure, treatments focus on managing symptoms and improving quality of life:
- Medications: To control symptoms like seizures, pain, or muscle stiffness.
- Physical Therapy: Enhances mobility and strengthens muscles.
- Occupational Therapy: Assists in adapting daily activities to accommodate physical limitations.
- Speech Therapy: Helps with communication difficulties.
- Psychological Support: Provides coping strategies for emotional challenges.
5. Managing the Condition
5.1 Coping Strategies
- Support Groups: Connecting with others facing similar challenges can provide emotional support.
- Counseling: Professional help to manage feelings of depression, anxiety, or stress.
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Practices like meditation or yoga can reduce stress and improve mental well-being.
5.2 Lifestyle Adjustments
- Healthy Diet: Proper nutrition supports overall health and energy levels.
- Regular Exercise: Tailored physical activity can enhance mobility and reduce symptoms.
- Adequate Rest: Ensuring sufficient sleep to help the body recover and maintain energy.
- Adaptive Devices: Using tools like wheelchairs, walkers, or communication aids to improve independence.
6. Health Professionals Who Can Help
A multidisciplinary approach is often necessary to effectively manage rare neurological disorders. Key health professionals include:
- Neurologist: A doctor specializing in nervous system disorders.
- Genetic Counselor: Provides information and support regarding genetic aspects of the disorder.
- Physical Therapist: Assists with improving movement and physical function.
- Occupational Therapist: Helps adapt daily activities and environments for better functionality.
- Speech-Language Pathologist: Supports communication and swallowing difficulties.
- Psychologist or Psychiatrist: Offers mental health support and treatment.
- Social Worker: Aids in accessing resources and support services.
7. Things to Avoid
Managing a rare neurological disorder involves certain precautions to prevent exacerbating the condition:
- Avoiding Triggers: Identifying and steering clear of factors that worsen symptoms, such as stress, excessive heat, or specific allergens.
- Ignoring Symptoms: Promptly addressing new or worsening symptoms with a healthcare provider.
- Overexertion: Balancing activity with rest to prevent fatigue and physical strain.
- Isolation: Maintaining social connections to support emotional well-being.
- Inconsistent Medication Use: Adhering to prescribed treatment plans without skipping doses.
Understanding the nervous system and the impact of rare neurological disorders is the first step toward effective management and improved quality of life. Collaborating with healthcare professionals and utilizing available resources can make a significant difference in navigating these challenges.