Importance of Skin Exams
Regular skin exams are crucial for the early detection of rare skin cancers. Detecting cancer early increases the chances of successful treatment and can prevent the disease from spreading.
- Early Detection: Identifying skin cancer in its initial stages can lead to more effective treatment options.
- Regular Check-ups: Scheduling routine skin exams with a healthcare professional helps monitor any changes in your skin over time.
What to Expect During a Skin Exam
Understanding what happens during a skin exam can help ease any anxiety you may have.
Self-Exam Guidelines
Performing regular self-exams allows you to monitor your skin for any unusual changes.
- How to Examine: Use a mirror to check your entire body, including hard-to-see areas like your back, scalp, and between toes.
- What to Look For: Notice any new growths, changes in existing moles, or areas that look different from the surrounding skin.
Professional Skin Examinations
A professional skin exam is conducted by a dermatologist or other qualified healthcare provider.
- Comprehensive Check: The doctor will examine your skin, hair, and nails for any signs of cancer.
- Detailed Assessment: They may use special tools to get a closer look at suspicious areas.
Diagnostic Techniques
Various techniques are used to accurately diagnose rare skin cancers.
Visual Inspection
The first step in diagnosing skin cancer involves a thorough visual examination.
- Assessment of Appearance: The doctor looks for irregular shapes, colors, or sizes that may indicate cancer.
- Symmetry and Borders: Irregular borders and asymmetrical shapes can be signs of malignancy.
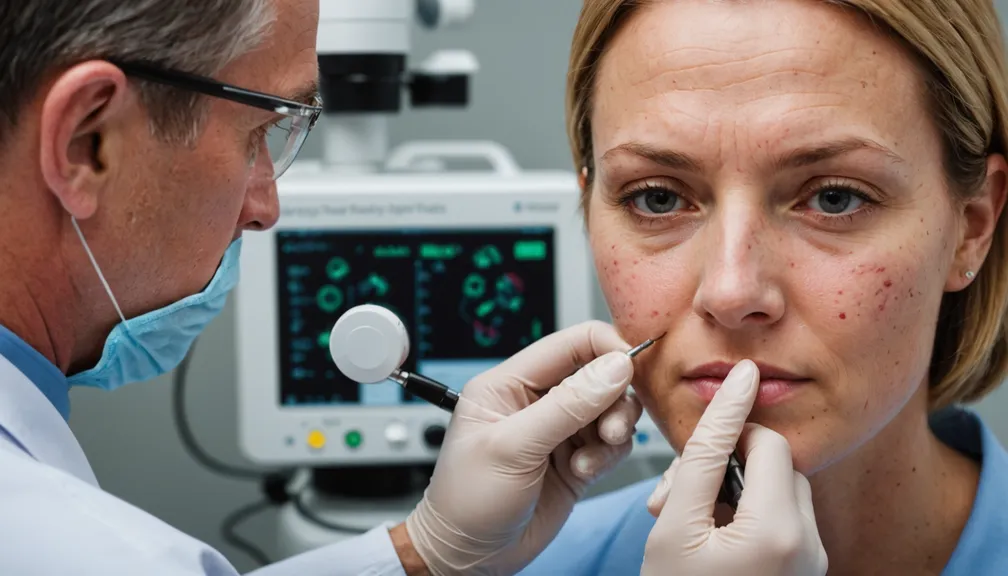
Dermatoscopy
Dermatoscopy is a non-invasive technique that provides a magnified view of the skin.
- Enhanced Visualization: Using a dermatoscope, the doctor can see deeper layers of the skin.
- Pattern Recognition: Helps in identifying patterns that are characteristic of certain types of skin cancer.
Total Body Photography
This method involves taking photographs of your skin to track changes over time.
- Documentation: High-resolution images help in monitoring existing moles and lesions.
- Comparison: Allows for easy comparison during future exams to detect any new or changing spots.
Biopsy Procedures
If a suspicious area is found, a biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis.
Types of Biopsies
Different biopsy methods are used depending on the size and location of the suspicious area.
- Punch Biopsy
- Procedure: A small, circular tool is used to remove a deep sample of skin.
-
Use: Suitable for small, raised spots or if deeper layers need examination.
-
Shave Biopsy
- Procedure: A tool is used to shave off the top layers of the skin.
-
Use: Ideal for flat or slightly raised lesions.
-
Excisional Biopsy
- Procedure: The entire suspicious area is removed along with a margin of healthy skin.
- Use: Preferred for larger or more suspicious growths to ensure complete removal.
What to Expect During a Biopsy
Understanding the biopsy process can help you prepare for the procedure.
- Preparation: The area will be cleaned, and a local anesthetic will be applied to numb the site.
- Procedure: The doctor will remove a small sample of skin using one of the biopsy methods.
- Aftercare: The area may be bandaged, and instructions will be provided for care during healing.
Recovery and Aftercare
Proper care after a biopsy is essential for healing and reducing the risk of infection.
- Keep the Area Clean: Follow your doctor's instructions on how to care for the biopsy site.
- Watch for Signs of Infection: Redness, swelling, or increased pain should be reported to your healthcare provider.
- Follow-Up Appointments: Attend all scheduled appointments to discuss biopsy results and next steps.
Understanding Biopsy Results
Receiving and understanding your biopsy results is a critical step in managing rare skin cancer.
Interpreting Findings
Your doctor will explain the results of your biopsy in clear, understandable terms.
- Positive Diagnosis: If cancer cells are found, the type and stage of cancer will be determined.
- Negative Diagnosis: If no cancer is detected, your doctor may suggest continued monitoring.
Next Steps after Diagnosis
Depending on the biopsy results, your treatment plan will be outlined.
- Treatment Options: May include surgery, radiation therapy, or other treatments tailored to your specific condition.
- Additional Testing: Further tests may be necessary to assess the extent of the cancer.
Healthcare Professionals Involved
A team of specialized healthcare providers collaborates to provide comprehensive care for rare skin cancers.
- Dermatologists: Specialists in skin health who perform skin exams and biopsies.
- Oncologists: Doctors who manage cancer treatment plans.
- Pathologists: Medical professionals who analyze biopsy samples to provide a diagnosis.
- Surgeons: Surgeons may perform excisional biopsies or remove cancerous tissue.
- Nurses and Support Staff: Provide care, support, and education throughout your treatment journey.
Preparing for Your Appointment
Being prepared for your skin exam and potential biopsy can help the process go smoothly.
Questions to Ask Your Doctor
Having a list of questions ensures you get all the information you need.
- What are the signs of rare skin cancer I should watch for?
- How often should I have skin exams?
- What does the biopsy procedure involve?
- What are the possible risks and benefits of the biopsy?
Information to Provide
Share relevant information with your healthcare provider to aid in accurate diagnosis and treatment.
- Medical History: Inform about any previous skin issues or cancers.
- Family History: Mention if any family members have had skin cancer.
- Current Medications: Provide a list of all medications and supplements you are taking.
Understanding the diagnostic techniques involved in detecting and confirming rare skin cancers empowers you to take an active role in your health care journey. Regular skin exams and knowing what to expect during biopsies are key steps in ensuring early detection and effective treatment.