Understanding Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Chronic Kidney Disease is a long-term condition where the kidneys gradually lose their ability to filter waste and excess fluids from the blood. Managing CKD effectively is essential to slow its progression and maintain a good quality of life.
1. Importance of Diet in Managing CKD
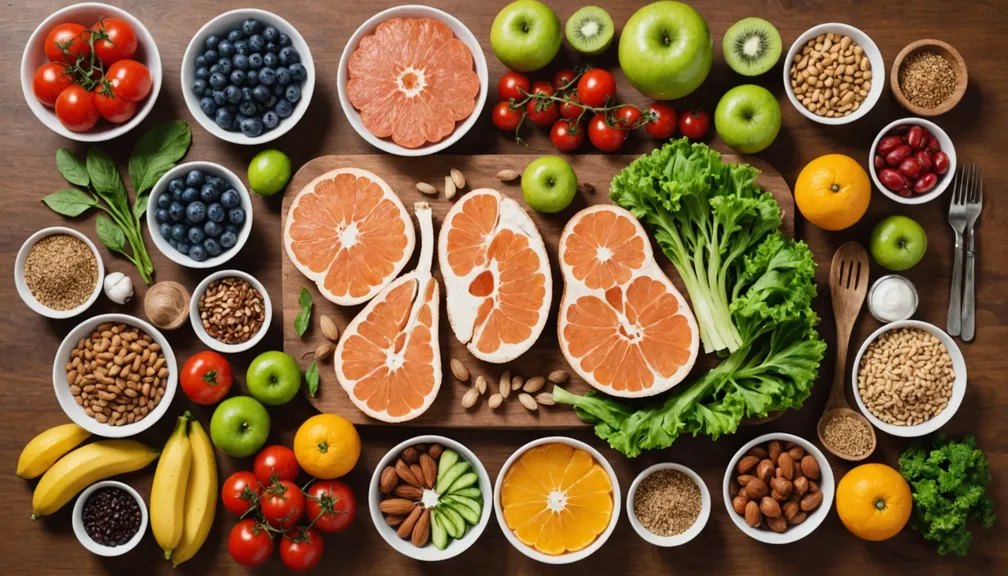
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in managing CKD. It helps control the buildup of waste products, manage blood pressure, and reduce the risk of complications.
a. Controlling Protein Intake
- Why It Matters: Excessive protein can strain the kidneys.
- Recommendations:
- Choose high-quality proteins such as lean meats, fish, and eggs.
- Limit red meat and processed meats.
- Consult a dietitian for personalized protein needs.
b. Managing Sodium Levels
- Why It Matters: High sodium can increase blood pressure and cause fluid retention.
- Recommendations:
- Aim for less than 2,300 mg of sodium per day.
- Avoid processed and packaged foods.
- Use herbs and spices for flavor instead of salt.
c. Controlling Potassium Intake
- Why It Matters: Too much potassium can affect heart function.
- Recommendations:
- Limit high-potassium foods like bananas, oranges, and potatoes.
- Choose lower-potassium alternatives such as apples, berries, and green beans.
- Monitor blood potassium levels regularly.
d. Balancing Phosphorus Levels
- Why It Matters: High phosphorus can weaken bones and lead to cardiovascular issues.
- Recommendations:
- Limit dairy products, nuts, and certain legumes.
- Choose phosphorus-free or low-phosphorus alternatives.
- Take phosphate binders if prescribed by your doctor.
2. Lifestyle Changes to Support Kidney Health
Adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly impact the progression of CKD and overall well-being.
a. Regular Physical Activity
- Benefits:
- Helps control weight.
- Lowers blood pressure.
- Improves cardiovascular health.
- Recommendations:
- Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week.
- Incorporate activities like walking, cycling, or swimming.
- Consult your healthcare provider before starting any new exercise regimen.
b. Maintaining a Healthy Weight
- Benefits:
- Reduces the risk of diabetes and high blood pressure.
- Decreases the strain on kidneys.
- Recommendations:
- Follow a balanced diet.
- Combine diet with regular physical activity.
- Seek support from a nutritionist if needed.
c. Quitting Smoking
- Benefits:
- Slows the progression of kidney disease.
- Reduces the risk of heart disease and cancer.
- Recommendations:
- Seek support programs or counseling.
- Consider medications to help quit smoking.
- Avoid environments where smoking is prevalent.
d. Limiting Alcohol Consumption
- Benefits:
- Prevents additional strain on kidneys and liver.
- Reduces the risk of high blood pressure.
- Recommendations:
- Limit alcohol intake to moderate levels (up to one drink per day for women and two for men).
- Choose non-alcoholic beverages when possible.
- Seek support if struggling with alcohol dependence.
3. Monitoring and Managing Blood Pressure
High blood pressure can accelerate kidney damage. Keeping it under control is vital for kidney health.
- Target Goals:
- Aim for a blood pressure below 130/80 mmHg.
- Strategies:
- Follow a low-sodium diet.
- Engage in regular physical activity.
- Take prescribed blood pressure medications consistently.
- Tools:
- Use a home blood pressure monitor.
- Keep a log of your readings to share with your healthcare provider.
4. Controlling Blood Sugar Levels
For patients with diabetes, managing blood sugar is essential to prevent kidney damage.
- Target Goals:
- Maintain Hemoglobin A1c levels as recommended by your doctor.
- Strategies:
- Follow a diabetes-friendly diet.
- Take insulin or other diabetes medications as prescribed.
- Monitor blood sugar levels regularly.
- Support:
- Work with an endocrinologist or diabetes educator.
- Join support groups for diabetes management.
5. Avoiding Harmful Substances and Practices
Certain substances and behaviors can worsen kidney function and overall health.
a. Over-the-Counter Medications
- Risks: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen can harm the kidneys.
- Recommendations:
- Always consult your doctor before taking any new medication.
- Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration if approved.
b. Herbal Supplements
- Risks: Some supplements can be toxic to the kidneys.
- Recommendations:
- Inform your healthcare provider about all supplements you are taking.
- Avoid unproven or non-regulated supplements.
6. Regular Medical Check-Ups and Monitoring
Staying on top of your health through regular check-ups is essential for managing CKD.
- What to Expect:
- Routine blood and urine tests to monitor kidney function.
- Blood pressure checks.
- Assessments for anemia and bone health.
- Frequency:
- Follow your doctor's recommendations, typically every 3-6 months.
- Benefits:
- Early detection of changes or complications.
- Timely adjustments to your management plan.
7. Support from Healthcare Professionals
Managing CKD involves a team of healthcare providers who can offer specialized care and support.
a. Nephrologist
- Role: A kidney specialist who oversees your CKD management plan, including medication and treatment strategies.
b. Dietitian
- Role: Provides personalized dietary plans to manage protein, sodium, potassium, and phosphorus intake.
c. Primary Care Physician
- Role: Coordinates overall health care, manages other chronic conditions, and monitors general health.
d. Diabetes Educator (if applicable)
- Role: Assists with blood sugar management and diabetes education to prevent further kidney damage.
e. Pharmacist
- Role: Reviews your medications for interactions and ensures you understand how to take them properly.
f. Social Worker or Counselor
- Role: Offers support for emotional challenges and helps navigate healthcare resources.
8. Building a Support System
Having a network of support can enhance your ability to manage CKD effectively.
- Ways to Build Support:
- Share your diagnosis and treatment plan with family and friends.
- Join support groups for individuals with kidney disease.
- Seek professional counseling if feeling overwhelmed.
- Benefits:
- Emotional support.
- Practical assistance with daily tasks.
- Shared experiences and coping strategies.
Managing Chronic Kidney Disease requires a comprehensive approach that includes dietary adjustments, lifestyle changes, regular monitoring, and support from healthcare professionals and loved ones. By taking proactive steps and working closely with your healthcare team, you can maintain your kidney function and improve your overall quality of life.