The Endocrine System: Hormones and Their Roles
Understanding the Endocrine System
What is the Endocrine System?
The endocrine system is a network of glands that produce and release hormones. These hormones travel through the bloodstream to regulate various functions in the body, including growth, metabolism, and mood.
Role of Hormones
Hormones act as chemical messengers, coordinating activities between different organs and tissues. They help maintain the body’s balance, known as homeostasis, ensuring that all bodily processes run smoothly.
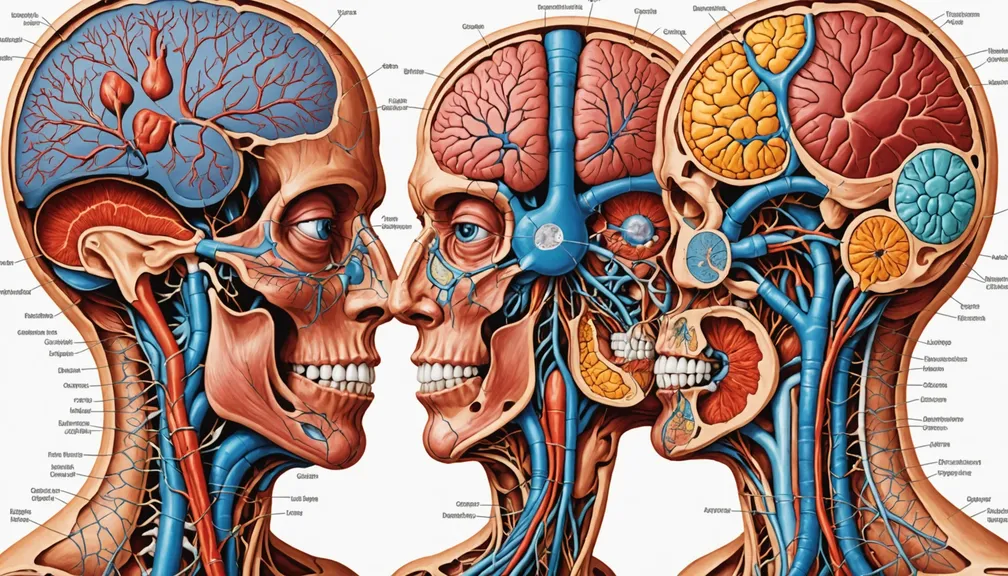
Common Hormone-Producing Glands
Pituitary Gland
Often called the "master gland," the pituitary gland controls other endocrine glands and regulates vital functions such as growth, blood pressure, and reproduction.
Thyroid Gland
Located in the neck, the thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism, energy levels, and body temperature.
Adrenal Glands
Situated above the kidneys, adrenal glands produce hormones that help the body respond to stress, regulate blood pressure, and manage electrolyte balance.
Pancreas
The pancreas plays a crucial role in regulating blood sugar levels by producing insulin and glucagon.
Gonads (Ovaries and Testes)
Gonads produce sex hormones like estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone, which are essential for reproductive health and secondary sexual characteristics.
What are Rare Endocrine Disorders?
Definition and Examples
Rare endocrine disorders are uncommon conditions that affect the hormone-producing glands. These disorders can disrupt the normal balance of hormones, leading to various health issues.
Examples of Rare Endocrine Disorders
- Addison's Disease: A disorder where the adrenal glands do not produce enough hormones, leading to symptoms like fatigue, weight loss, and low blood pressure.
- Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN): A group of disorders that cause tumors in multiple endocrine glands, affecting hormone levels and body functions.
Symptoms of Rare Endocrine Disorders
General Symptoms
- Unexplained weight loss or gain
- Extreme fatigue
- Mood swings or depression
- Abnormal growth patterns
- Changes in appetite
Specific Symptoms by Gland
- Adrenal Gland Disorders: Low blood pressure, darkening of the skin
- Thyroid Disorders: Changes in metabolism, sensitivity to temperature
- Pancreatic Disorders: Fluctuations in blood sugar levels, increased thirst
- Gonadal Disorders: Irregular menstrual cycles, reduced fertility
Diagnosis and Treatment
How Doctors Diagnose These Disorders
Diagnosis typically involves: - Medical History Review: Understanding symptoms and family history - Physical Examinations: Checking for physical signs of hormone imbalance - Blood Tests: Measuring hormone levels in the bloodstream - Imaging Studies: Using scans like MRI or CT to view gland structures
Treatment Options
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: Providing the body with the hormones it lacks
- Surgery: Removing tumors or affected glands when necessary
- Medications: Managing symptoms and regulating hormone levels
- Lifestyle Changes: Adopting a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management techniques
Living with a Rare Endocrine Disorder
Managing Symptoms
- Consistent Medication: Taking prescribed hormones or medications regularly
- Regular Check-Ups: Monitoring hormone levels and overall health with your healthcare team
- Balanced Diet: Eating nutritious foods to support hormone health
Lifestyle Changes
- Stress Management: Practicing relaxation techniques such as meditation or yoga
- Exercise: Engaging in regular physical activity to maintain energy levels and overall well-being
- Adequate Sleep: Ensuring sufficient rest to help the body function optimally
Support Systems
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who have similar conditions for emotional support
- Counseling: Seeking professional help to cope with the emotional aspects of living with a chronic condition
Healthcare Professionals Who Can Help
Endocrinologists
Specialists in hormone-related disorders, endocrinologists are the primary doctors managing rare endocrine conditions.
Primary Care Physicians
They provide general health care and coordinate with specialists to ensure comprehensive treatment.
Nurses and Nurse Practitioners
They offer support, administer treatments, and educate patients about managing their conditions.
Dietitians
Experts in nutrition, dietitians help create meal plans that support hormone balance and overall health.
Mental Health Professionals
Psychologists or counselors assist in managing the emotional and psychological challenges associated with chronic illnesses.
Understanding and managing a rare endocrine disorder involves a collaborative effort between patients, their loved ones, and a team of healthcare professionals. With the right support and treatment plan, individuals can lead fulfilling lives despite these complex conditions.